- What is a Polyethylene (PE) Pipe?
- What is a Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe?
- Key Differences Between Polyethylene and PVC Pipes
- Cost Comparison: Polyethylene Pipe vs PVC
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyethylene pipe vs PVC
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyethylene pipe vs PVC pipes
- Choosing the Right Polyethylene pipe vs pvc for Your Project Needs
- 9. Conclusion
Selecting the right piping material is critical to the success and longevity of a project. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial use, the type of pipe you choose can impact installation costs, maintenance, and the overall performance of your system. Two popular piping materials that often come up in these considerations are polyethylene pipe vs PVC. Both offer distinct advantages depending on the project’s requirements, but understanding their properties and applications is essential for making an informed decision. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive comparison of polyethylene pipe vs PVC, helping you determine which option is best suited to your project needs.
What is a Polyethylene (PE) Pipe?
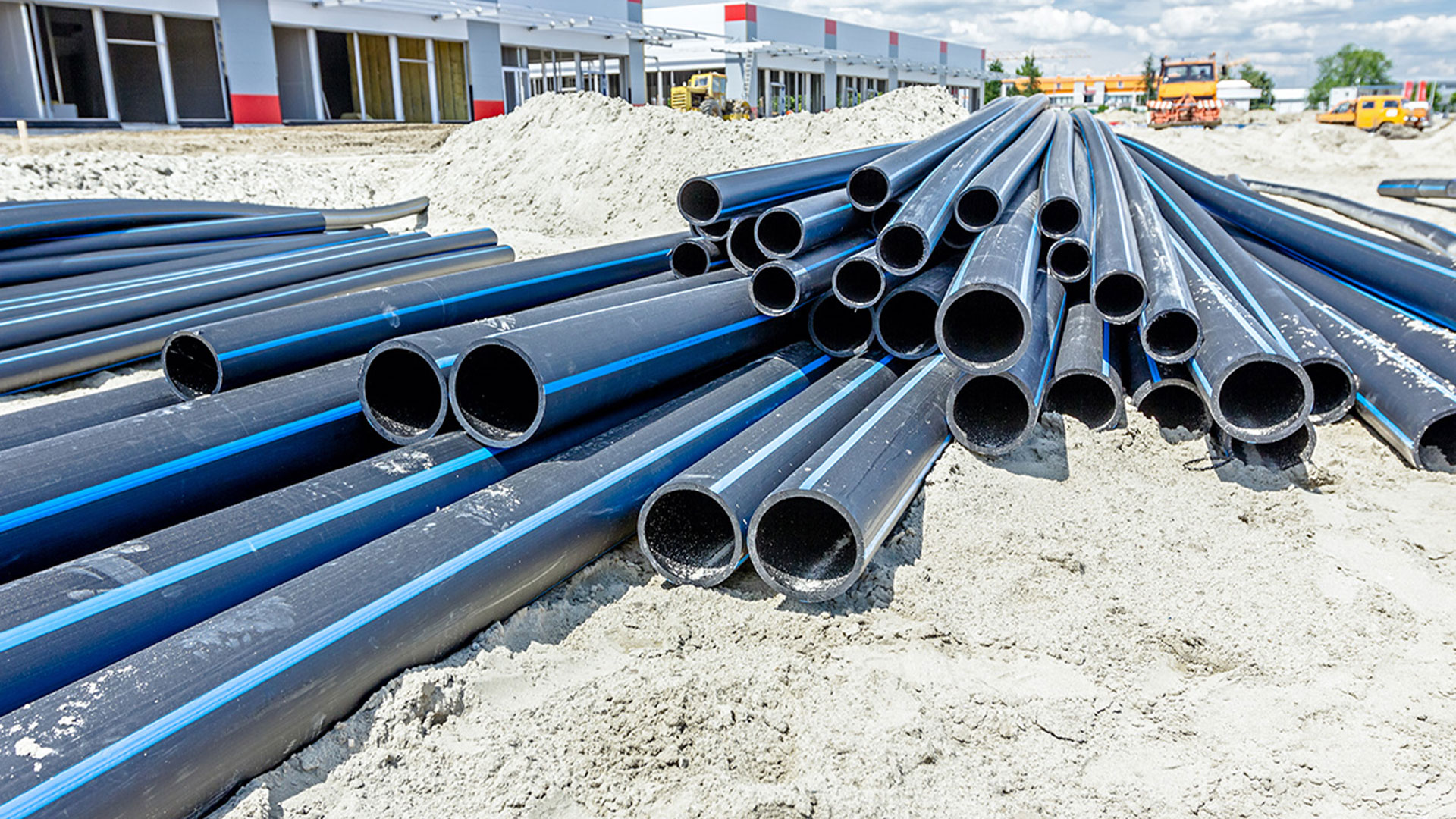

Polyethylene pipe vs pvc, commonly referred to as PE pipes, are made from polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer known for its durability and flexibility. PE pipes are typically available in three main forms: High Density Polyethylene pipe (HDPE) , Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE), and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). Each type has varying degrees of strength, flexibility, and resistance to pressure.
- HDPE is the strongest and most durable, and it is used in applications like water distribution and gas pipelines.
- MDPE is slightly less rigid than HDPE but still provides significant strength, commonly found in plumbing and irrigation systems.
- LDPE is more flexible and is often used in applications like low-pressure fluid transfer systems.
PE pipes are widely used in industries such as water supply, gas distribution, and irrigation systems. Their key properties include excellent flexibility, high resistance to chemicals, and the ability to withstand harsh weather conditions without degrading. This makes them ideal for projects requiring piping systems that can bend and shift with soil movement, resist chemical corrosion, and endure prolonged exposure to the elements.
What is a Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe?
Polyvinyl Chloride, or PVC, is another widely used thermoplastic polymer in the piping industry. PVC pipes come in two primary varieties: Unplasticized PVC (uPVC) and Chlorinated PVC (cPVC).
- uPVC is the most common type, and it is used for water supply and sewage systems due to its rigidity and resistance to corrosion.
- cPVC is designed for hot water systems, as it can withstand higher temperatures than standard uPVC.
PVC pipes are commonly found in plumbing, wastewater management, and electrical conduit applications. Their rigidity, fire resistance, and resistance to corrosion make them a go-to option for systems that require straight, unyielding pipes that won’t degrade easily when exposed to water or chemicals.
Key Differences Between Polyethylene and PVC Pipes
Understanding the fundamental differences between pipes can help determine which material is more suitable for your project.
Material Composition:
Pipes are thermoplastics, meaning they can be heated and molded into different shapes. However, their chemical structures differ, with PE being a simpler polymer that offers more flexibility, while PVC’s composition gives it increased rigidity and strength.
Flexibility and Rigidity:
PE is known for its flexibility, which allows it to be used in projects where the pipe needs to bend, such as in gas pipelines or irrigation systems. PVC, on the other hand, is much more rigid, making it ideal for applications like plumbing, where straight lines and stability are required.
Temperature Resistance:
When it comes to temperature resistance, PE performs better in extreme cold conditions, retaining its flexibility without becoming brittle. PVC is more resistant to high temperatures but can become brittle in freezing conditions, limiting its use in colder climates.
Pressure Ratings:
In terms of pressure tolerance, both materials offer good resistance. Still, high density polyethylene pipe generally has higher pressure ratings than PVC, making it a better choice for high-pressure applications like gas distribution.
Durability and Longevity:
Pipes are durable and can last for decades. However, PE tends to perform better in environments with fluctuating temperatures and soil conditions, while PVC’s rigidity makes it more vulnerable to cracking under stress.
Environmental Impact:
From an environmental perspective, both materials have their advantages and disadvantages. PE is recyclable, and its manufacturing process typically requires less energy than PVC. PVC, however, can be recycled but involves more energy-intensive production methods and may release harmful chemicals when burned.
Cost Comparison: Polyethylene Pipe vs PVC
When considering cost in the debate of polyethylene pipe vs PVC, PVC pipes tend to be more affordable upfront than PE pipes. However, the long-term costs can vary depending on the application and maintenance needs.
- Installation Costs: PVC is easier and cheaper to install due to its rigid structure, whereas PE may require more specialized installation methods to handle its flexibility.
- Maintenance Costs: PE generally requires less maintenance over time due to its resistance to chemicals and cracking, which can reduce long-term expenses.
- Long-Term Financial Benefits: Projects that require flexibility or are located in harsh environmental conditions may benefit from the durability of PE pipes despite their higher initial cost.
- Market Availability: Both materials are widely available, though pricing can fluctuate based on market trends and location.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyethylene pipe vs PVC
Advantages:
- High flexibility, ideal for applications that require movement or shifts in the piping system.
- Excellent resistance to chemicals and corrosion, making them suitable for gas distribution and water supply in harsh environments.
- Durability in extreme weather conditions, including freezing temperatures.
- Lower susceptibility to cracking under pressure.
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial costs compared to PVC.
- Installation challenges due to its flexibility, which may require specialized techniques.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyethylene pipe vs PVC pipes
Advantages:
- It is more affordable than PE, making it a cost-effective solution for many projects.
- Easy to install thanks to its rigid structure, reducing labor costs.
- It is resistant to chemical wear and tear, making it a reliable choice for plumbing and wastewater systems.
Disadvantages:
- Brittle and prone to cracking under stress or when exposed to freezing temperatures.
- Limited temperature tolerance, making it less suitable for extremely hot or cold environments.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene pipe vs pvc for Your Project Needs
When selecting between polyethylene pipe vs PVC, several factors should be considered:
- Project Type: The specific use (e.g., water supply, gas distribution, or electrical conduit) will heavily influence which material is more appropriate.
- Environmental Conditions: Due to its flexibility, PE may be the better choice if your project is located in an area with fluctuating temperatures or challenging soil conditions.
- Budget Constraints: While PVC may offer lower upfront costs, the long-term savings of using PE in specific applications may justify the higher initial investment.
9. Conclusion
In summary, both polyethylene and PVC pipes offer significant advantages depending on the project’s requirements. Polyethylene pipe vs PVC is a common comparison, but the decision ultimately depends on factors such as flexibility, durability, temperature resistance, and cost. Polyethylene, particularly high density polyethylene pipe, is more flexible, durable in extreme environments, and resistant to chemicals, making it ideal for gas and water supply systems. PVC, on the other hand, is more affordable, easier to install, and performs well in low-pressure, stable environments like plumbing and wastewater systems.






0 Comments